 En este capítulo vamos a ver como conectar un “Display” numérico con 4 dígitos de 7 segmentos. Esto nos permitirá mostrar 4 números del 0 al 9 para mostrar información de la Raspberry, como por ejemplo, un reloj, un contador, un cronómetro, etc.
En este capítulo vamos a ver como conectar un “Display” numérico con 4 dígitos de 7 segmentos. Esto nos permitirá mostrar 4 números del 0 al 9 para mostrar información de la Raspberry, como por ejemplo, un reloj, un contador, un cronómetro, etc.
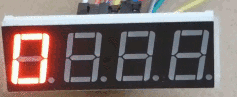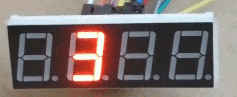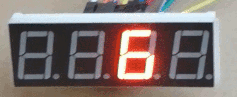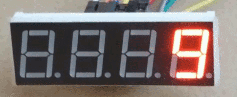


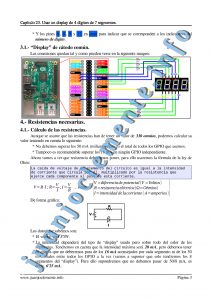
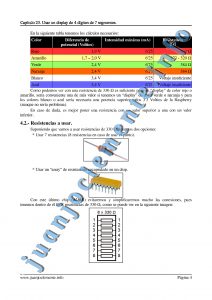



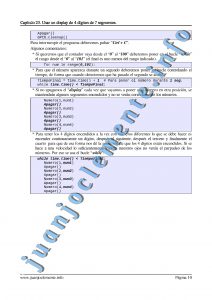
Fichero “Pruebas.py”:
# Fichero “Pruebas.py”:
# Importamos la librerias necesarias
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
# Inicializaciones
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# Constantes globales para ENCENDER o APAGAR un segmento
SegEncender=True
SegApagar=False
# Constantes globales para ACTIVAR o DESACTIVAR un dígito
DigEncender=False
DigApagar=True
# GPIO para los segmentos del DISPLAY:
SegA=24
SegB=18
SegC=20
SegD=16
SegE=12
SegF=23
SegG=21
SegP=25
# GPIO para los DÍGITOS del DISPLAY:
Dig1=22
Dig2=27
Dig3=17
Dig4=5
# Asigno los SEGMENTOS a los GPIO para el DISPLAY:
GPIO.setup(SegA, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento A.
GPIO.setup(SegB, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento B.
GPIO.setup(SegC, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento C.
GPIO.setup(SegD, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento D.
GPIO.setup(SegE, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento E.
GPIO.setup(SegF, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento F.
GPIO.setup(SegG, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento G.
GPIO.setup(SegP, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento P.
# Asigno los DÍGITOS a los GPIO para el DISPLAY:
GPIO.setup(Dig1, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento A.
GPIO.setup(Dig2, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento B.
GPIO.setup(Dig3, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento C.
GPIO.setup(Dig4, GPIO.OUT) # Segmento D.
# Funciones del programa:
def Encender(): # ENCIENDE todos los SEGMENTOS.
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegEncender) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegEncender) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
def Apagar(): # APAGA todos los SEGMENTOS.
GPIO.output(SegA, SegApagar) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegApagar) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegApagar) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegApagar) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegApagar) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegApagar) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegApagar) # Segmento G.
def Numero(dig,num): # Pone el DÍGITO y el NÚMERO que se le envía
# Activo el DÍGITO correspondiente: ########################
if dig == 1:
print('Dígito 1')
GPIO.output(Dig1, DigEncender) # Dígito 1
GPIO.output(Dig2, DigApagar) # Dígito 2
GPIO.output(Dig3, DigApagar) # Dígito 3
GPIO.output(Dig4, DigApagar) # Dígito 4
elif dig == 2:
print('Dígito 2')
GPIO.output(Dig1, DigApagar) # Dígito 1
GPIO.output(Dig2, DigEncender) # Dígito 2
GPIO.output(Dig3, DigApagar) # Dígito 3
GPIO.output(Dig4, DigApagar) # Dígito 4
elif dig == 3:
print('Dígito 3')
GPIO.output(Dig1, DigApagar) # Dígito 1
GPIO.output(Dig2, DigApagar) # Dígito 2
GPIO.output(Dig3, DigEncender) # Dígito 3
GPIO.output(Dig4, DigApagar) # Dígito 4
elif dig == 4:
print('Dígito 4')
GPIO.output(Dig1, DigApagar) # Dígito 1
GPIO.output(Dig2, DigApagar) # Dígito 2
GPIO.output(Dig3, DigApagar) # Dígito 3
GPIO.output(Dig4, DigEncender) # Dígito 4
else :
print('ERROR en el dígito')
GPIO.output(Dig1, DigApagar) # Dígito 1
GPIO.output(Dig2, DigApagar) # Dígito 2
GPIO.output(Dig3, DigApagar) # Dígito 3
GPIO.output(Dig4, DigApagar) # Dígito 4
# Pongo el NÚMERO. ####################################
if num == 0:
print('Pongo el 0')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegEncender) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegEncender) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegApagar) # Segmento G.
elif num == 1:
print('Pongo el 1')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegApagar) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegApagar) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegApagar) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegApagar) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegApagar) # Segmento G.
elif num == 2:
print('Pongo el 2')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegApagar) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegEncender) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegApagar) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
elif num == 3:
print('Pongo el 3')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegApagar) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegApagar) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
elif num == 4:
print('Pongo el 4')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegApagar) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegApagar) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegApagar) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegEncender) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
elif num == 5:
print('Pongo el 5')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegApagar) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegApagar) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegEncender) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
elif num == 6:
print('Pongo el 6')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegApagar) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegEncender) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegEncender) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
elif num == 7:
print('Pongo el 7')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegApagar) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegApagar) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegApagar) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegApagar) # Segmento G.
elif num == 8:
print('Pongo el 8')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegEncender) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegEncender) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
elif num == 9:
print('Pongo el 9')
GPIO.output(SegA, SegEncender) # Segmento A.
GPIO.output(SegB, SegEncender) # Segmento B.
GPIO.output(SegC, SegEncender) # Segmento C.
GPIO.output(SegD, SegEncender) # Segmento D.
GPIO.output(SegE, SegApagar) # Segmento E.
GPIO.output(SegF, SegEncender) # Segmento F.
GPIO.output(SegG, SegEncender) # Segmento G.
else: # Por si recibo otro valor
print('Apago todo')
Apagar()
####################################################
### Código principal de la página:
####################################################
# Bucle infinito con el programa:
try:
while True:
for dig in [1,2,3,4]:
for num in [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]:
Numero(dig,num)
print('DÍGITO: {} NÚMERO: {}'.format(dig,num))
time.sleep(1)
# Atrapa la pulsación de teclado: CTRL+C para acabar
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('Apago todo para terminar')
Apagar()
GPIO.cleanup()
Fichero “contador.py”:
# Fichero “contador.py”:
:
:
: El mismo contenido del ejemplo anterior,
: hasta la función “Numero()” incluida.
:
:
def PonerNumero(num): # Descompone el número y lo envía al "display"
num4 = num % 10
num3 = (num // 10) % 10
num2 = (num // 100) % 10
num1 = (num // 1000) % 10
TiempoFinal = time.time() + 1 # Pone el número durante 1 seg.
while time.time() < TiempoFinal:
Numero(1,num1)
Apagar()
Numero(2,num2)
Apagar()
Numero(3,num3)
Apagar()
Numero(4,num4)
Apagar()
####################################################
### Código principal de la página:
####################################################
# Bucle infinito con el programa:
try:
while True:
for num in range(0,101):
print('NÚMERO: {}'.format(num))
PonerNumero(num)
# Atrapa la pulsación de teclado: CTRL+C para acabar
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('Apago todo para terminar')
Apagar()
GPIO.cleanup()
| Capítulo Anterior | Capítulo Siguiente |
